What is Posterior Uveitis? Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
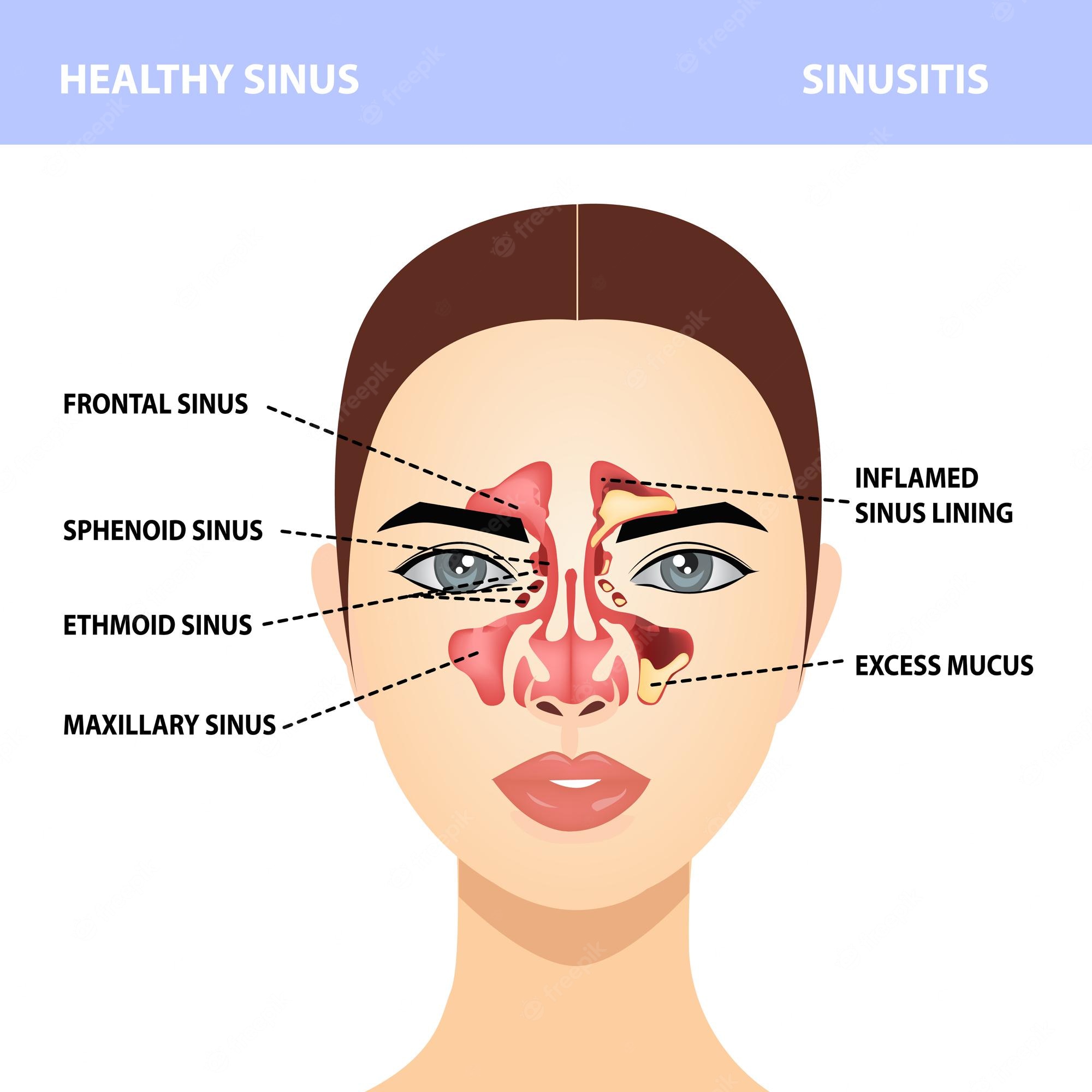
Posterior uveitis (PU) is commonly called red-eye disease. This is also known as end-stage uveitis, posterior segment inflammation or choroiditis. It is a disease that affects the innermost part of your eye – known as the posterior segment. The posterior segment of the eye includes various structures such as the choroid, optic nerve, and blood vessels.
It is characterized by inflammation in these areas and the cause can be anything from a virus to bacteria or parasites. The redness of your eyes will be caused by swelling of the blood vessels located in that area of your eyes. This article will let you know about this condition in detail, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment methods.
What is Posterior Uveitis?
Posterior uveitis is commonly called red-eye disease. This is also known as end-stage uveitis, posterior segment inflammation or choroiditis. It is a disease that affects the innermost part of your eye – known as the posterior segment. The posterior segment of the eye includes various structures such as the choroid, optic nerve, and blood vessels.
The uvea is a thin membrane located between the retina and the sclera. In this layer, there is the choroid, ciliary body, and iris. The choroid is responsible for supplying the retina with blood and nutrients and also removes waste products.
The ciliary body is responsible for the production of aqueous humor, an important part of the eye’s internal fluid. The iris is responsible for controlling the amount of light that gets into the eye by regulating the size of the pupil.
Causes of Posterior Uveitis
Bacterial infection: It is the most common cause of uveitis, which can be triggered by infections like gonorrhea, syphilis, or tuberculosis.
Fungal infection: Fungal infections like blastomycosis and histoplasmosis can also cause uveitis.
Parasitic infection: Parasitic infections like toxoplasmosis, Schistosomiasis, and Onchocerciasis can lead to uveitis.
Viral infection: Viral infections like herpes simplex, herpes zoster, and cytomegalovirus can cause uveitis. In some cases, uveitis is not associated with any infection and is caused due to some other reasons.
Symptoms of Posterior Uveitis
The symptoms of uveitis depend on the part of the eye where the inflammation is present. The symptoms can vary from person to person. If the inflammation is present in the front part of your eyes, then you will experience itching of your eyelids, frequent watery eyes, and a fluctuation in intraocular pressure.
The symptoms of posterior uveitis include:
Redness of the eyes: A redness of the eyes is the most common symptom of uveitis. This redness is caused by the blood vessels located in that part of your eyes and can last for a long time.
Eye pain: Some people may experience a pain in their eyes.
Blurred vision: You might notice that you can’t see things clearly.
Discharge from the eyes: There can be a discharge from the eyes, which can be either clear or yellowish in color.
Diagnosis of Posterior Uveitis
The doctor will examine your eyes, and check for redness and inflammation in the retina, choroid, and ciliary body. He will ask you several questions regarding your medical history and the symptoms you are experiencing. He will also check your intraocular pressure. Depending on the results of the examination and the test results, the doctor will diagnose the condition.
The following tests are usually performed to diagnose uveitis
Examination: The doctor will first check your eyes and look for the signs of inflammation.
Blood test: Your doctor may order a blood test to check whether there is an infection in your body.
Intraocular pressure test: This test is performed to check the pressure inside the eyes. Bacterial and viral cultures: The doctor may take a sample from the eye and check for the presence of any infection.
Treatment of Posterior Uveitis
Treatment for posterior uveitis depends on the underlying cause of the condition. The treatment can be done either with medications or with surgery.
The doctor may recommend the following treatments
Antibiotics: Antibiotics are the most common treatment followed in uveitis. Depending on the type of infection causing the disease, your doctor will prescribe you an antibiotic.
Painkillers: If you are experiencing pain in your eyes, you can use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to get relief from the pain.
Immunosuppressants: In certain cases, immunosuppressants are prescribed to control inflammation and swelling.
Surgery: In rare cases, surgery is performed to remove inflamed tissues.
Conclusion
Uveitis is a disease that causes inflammation in the eye. The symptoms of uveitis include redness of the eyes, blurred vision, and pain. Posterior uveitis affects the back part of the eye, and the common causes are bacterial, fungal, and parasitic infections.
The doctor will perform a test to diagnose uveitis and prescribe medications to treat the condition. If you are experiencing any of the above symptoms, then you must consult a doctor immediately. The doctor will perform a test, and depending on the results, will recommend a treatment. You must take the prescribed medications exactly as suggested by the doctor to get relief from the symptoms of uveitis